The efficacy of minocycline hydrochloride ointment versus iodoform gauze for alveolar osteitis: A prospective cohort study, BMC Oral Health
$ 14.00 · 4.5 (406) · In stock
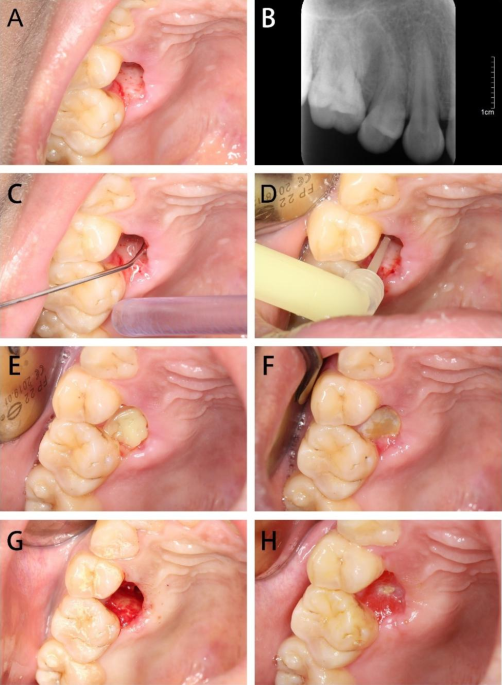
Background Alveolar osteitis (AO) is one of the most commonly encountered complication following tooth extraction, however, to date there is no standard methods of prevention and treatment. The study aims to investigate the efficiency of minocycline hydrochloride ointment (MHO) for the treatment of alveolar osteitis compared with traditional treatment with iodoform gauze (IG). Methods/design STROBE checklist was followed to report this study. All patients underwent tooth extraction either in our department or other hospitals, whom presented with postoperative pain, were screened out to meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria of this study about AO. Patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were enrolled in our prospective cohort study, and MHO or IG was administered. The Visual analog scale scores were used to assess the pain score of patients. The healing status of the extraction sockets was followed up. Differences in responses between groups were analyzed using Mann-Whitney U tests. Chi-square test was performed to explore the differences in the teeth position of AO. Results Of 41,371 patients underwent tooth extraction with post-operative follow-up in our departments, only 20 patients (0.05%) suffered from AO. 31 patients with AO, whose teeth were extracted in other places, were also enrolled. The incidence of AO was significantly higher in third molars than other teeth (P < 0.01). In 28 patients that were treated with MHO, the pain was relieved substantially on day 3 and almost painless on day 7. And only 25% of cases required dressing change more than once. Whilst 23 patients treated with IG, the pain was relieved on day 5, and 56.5% of cases required multiple dressing change. The difference between the two groups of VAS scores had statistical significance during treatment at 8 h, 24 h, 3d, 5d, and 7d. No allergic reaction or further infection occurred. Conclusion MHO has a safer and higher therapeutic effect in the treatment of AO compared with traditional treatment with IG. MHO may become a preferred treatment modality for AO.

Minocycline and Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator for Stroke

The efficacy of chlorhexidine gel in the prevention of alveolar
Retreatments Solutions For Periapical Diseases of Endodontic

Antibiotics, Free Full-Text
![]()
Clinical effect of minocycline hydrochloride ointment on canine

Additional file 1 of The efficacy of minocycline hydrochloride

Outcomes of Babies with Opioid Exposure (OBOE): protocol of a
Clinical Efficacy of Minocycline Hydrochloride for the Treatment
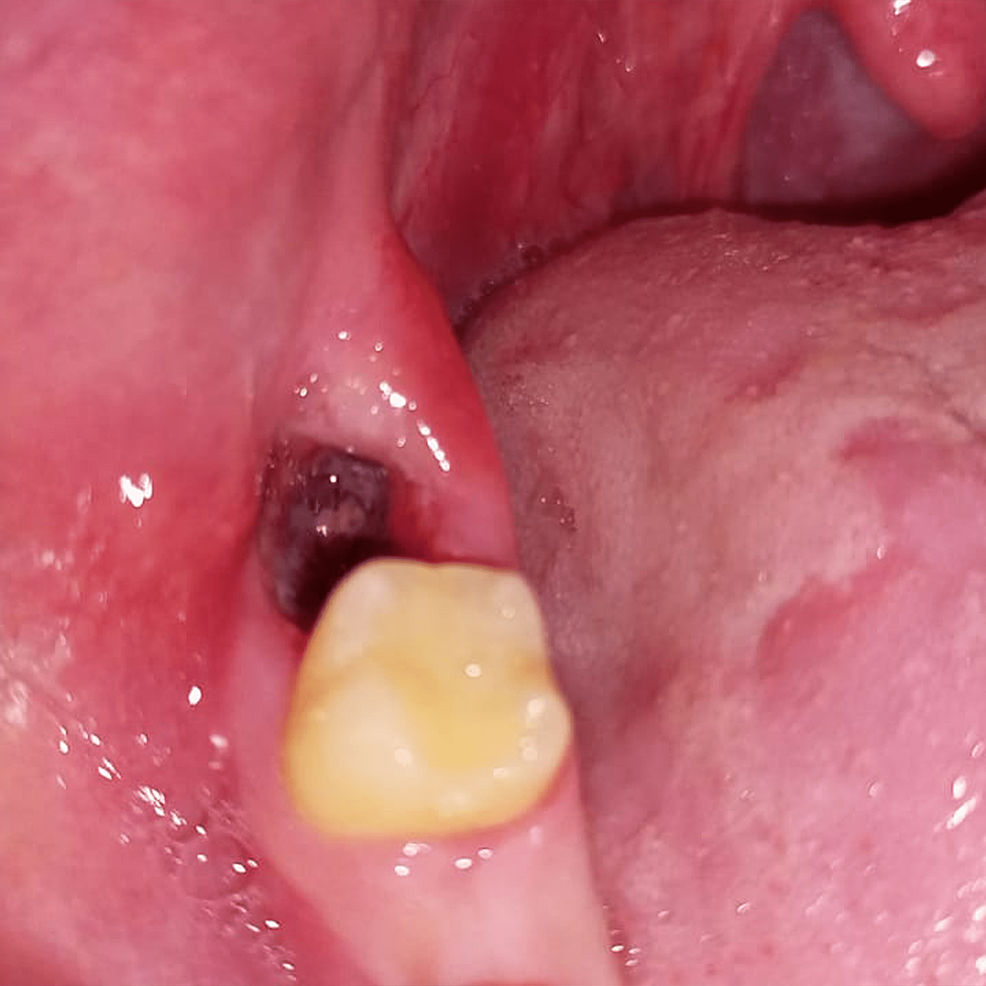
Alveolar Osteitis: Etiology, Prevention, And Treatment, 49% OFF

VAS scores of patients in both groups after treatment
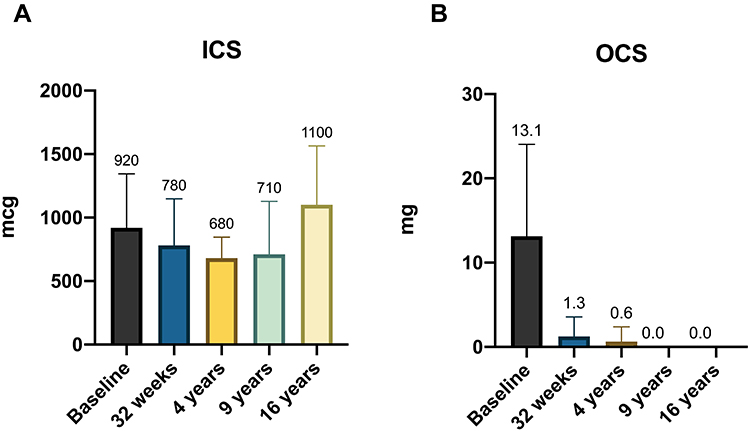
Efficacy and safety of omalizumab treatment over a 16-year
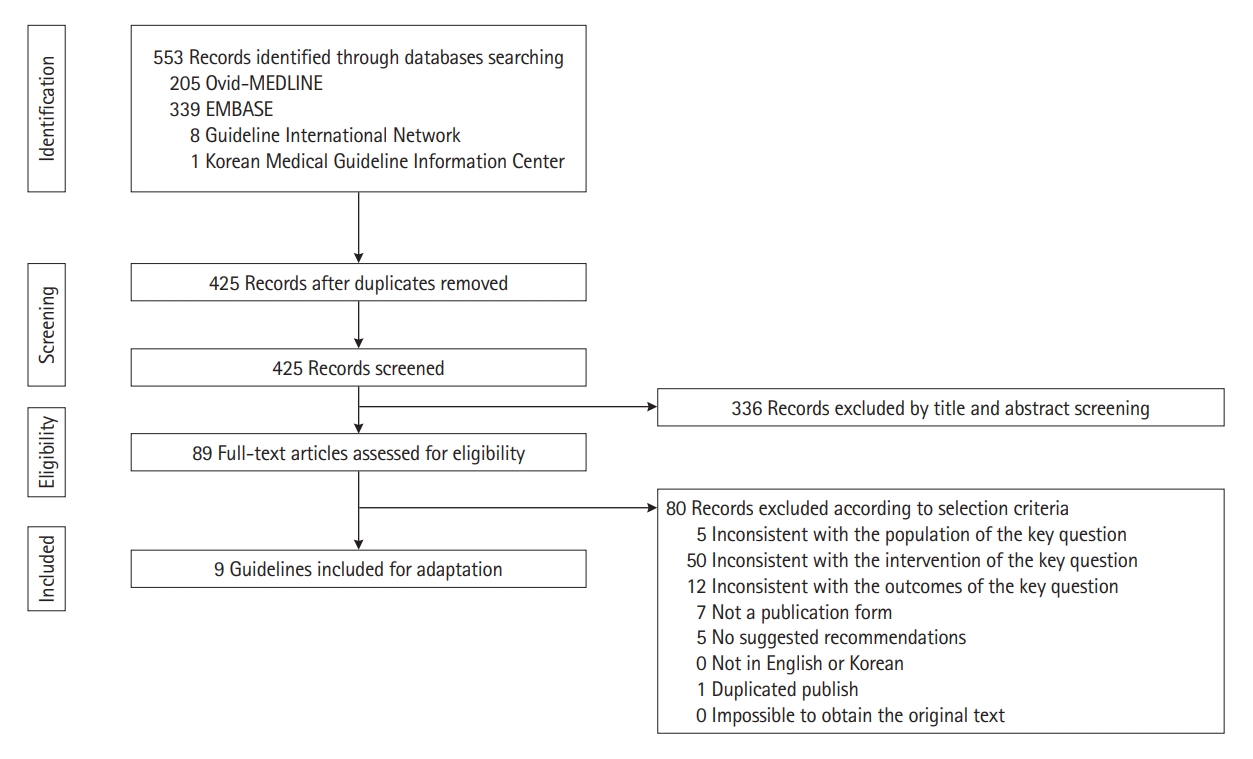
Korean clinical practice guidelines on biologics and small

Cost-effectiveness of a 12-month fixed-duration venetoclax

Randomized controlled trial of pilocarpine hydrochloride for the










